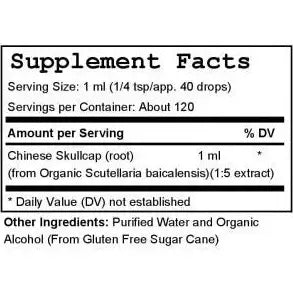
Chinese Skullcap
Chinese Skullcap
Couldn't load pickup availability
Scutellaria baicalensis is a medicinal plant deeply rooted in traditional Chinese medicine. The plant contains various bioactive compounds, such as baicalin and baicalein, which exhibit notable antimicrobial properties against a range of pathogens, including those associated with tick-borne diseases. Research has shown that Scutellaria baicalensis extracts may hinder the growth and dissemination of Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, suggesting a potential role in combating the infection. Additionally, the plant’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties may aid in reducing the inflammatory responses and oxidative stress triggered by tick-borne pathogens, potentially alleviating the severity of symptoms. However, further comprehensive studies, including clinical trials, are necessary to validate the safety and efficacy of Scutellaria baicalensis as a therapeutic option for Lyme disease and tick-borne illnesses.
Properties:
- Antimicrobial Activity: Baikal skullcap contains several bioactive compounds, including flavonoids such as baicalin and baicalein, which exhibit antimicrobial properties. While the direct impact on tick-borne bacteria is not well-established, the antimicrobial activity of Baikal skullcap suggests potential benefits in addressing infections associated with tick-borne diseases.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Baikal skullcap has been found to possess anti-inflammatory properties. In tick-borne diseases, inflammation plays a significant role in the development of symptoms and tissue damage. By reducing inflammation, Baikal skullcap may help alleviate some of these effects.
- Immune Modulation: Baikal skullcap has been shown to have immunomodulatory effects, meaning it can help regulate and balance the immune response. Tick-borne diseases can both suppress and over activate the immune system, and immune modulation may be beneficial in restoring immune function.
- Antioxidant Effects: Baikal skullcap contains antioxidants that can help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. Tick-borne diseases can generate oxidative stress, leading to tissue damage and inflammation. Antioxidants can potentially mitigate these effects and support overall health.
Research:
- “In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi against Borrelia burgdorferi” (2014): This study investigated the antibacterial activity of Scutellaria baicalensis extract against Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacteria responsible for Lyme disease. The researchers found that the extract demonstrated significant inhibitory effects on the bacteria, suggesting its potential as a natural antibacterial agent.
- “Baicalein, an Active Component of Scutellaria baicalensis, Inhibits the Inflammatory Response and Symptom Severity of Lyme Arthritis” (2017): This study explored the effects of baicalein, a major bioactive compound found in Scutellaria baicalensis, on Lyme arthritis—an inflammatory condition associated with Lyme disease. The researchers found that baicalein reduced joint inflammation and improved symptoms in a mouse model of Lyme arthritis, suggesting its potential as an anti-inflammatory agent in the context of tick-borne diseases.
- “Scutellaria baicalensis Inhibits the Pathogen-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Responses in Human THP-1-Derived Macrophages” (2018): This study investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of Scutellaria baicalensis extract on human macrophages in response to infection with tick-borne pathogens. The researchers found that the extract suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduced inflammatory responses, indicating its potential in modulating immune responses associated with tick-borne diseases

Share