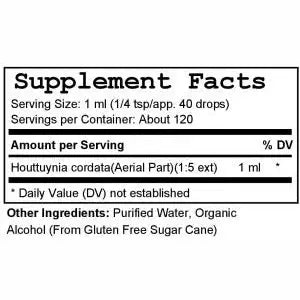
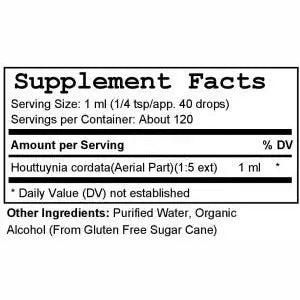
Houttuynia
Houttuynia
Couldn't load pickup availability
Houttuynia cordata, commonly known as fish mint or heartleaf, has been of interest in the context of Lyme disease and tick-borne illnesses due to its diverse bioactive components. The plant contains flavonoids, alkaloids, and essential oils, some of which have demonstrated antimicrobial properties against various pathogens, including those associated with tick-borne diseases. Studies have shown that Houttuynia cordata extracts may exhibit inhibitory effects against Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, suggesting potential therapeutic benefits. Additionally, the plant’s constituents have displayed anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities, which may be instrumental in reducing inflammation and supporting the immune response against tick-borne infections.
Properties:
- Antimicrobial Properties: Houttuynia cordata has been found to possess antimicrobial properties against a range of bacteria, fungi, and parasites. While its direct effects on tick-borne pathogens have not been extensively studied, its antimicrobial activity suggests potential benefits in addressing infections associated with tick-borne diseases.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Inflammation is a key contributor to symptoms and tissue damage in tick-borne diseases. Houttuynia cordata has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which may help alleviate inflammation associated with these diseases.
- Immunomodulatory Effects: Tick-borne diseases can dysregulate the immune system, leading to an imbalance in immune responses. Houttuynia cordata has been found to have immunomodulatory effects, which can help regulate and balance the immune response. This may be relevant in managing tick-borne diseases.
- Antioxidant Effects: Houttuynia cordata contains antioxidant compounds that help neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. Tick-borne diseases can induce oxidative stress, leading to tissue damage and inflammation. Antioxidants may have a protective effect in this context.
While Houttuynia cordata has been studied for its potential health benefits and traditional uses, the available scientific literature does not provide direct research on its effects on tick-borne diseases or its specific interactions with tick-borne pathogens.

Share